Pipe tapered screws gauge do not have a pass/stop division. gauge There is a notch (step) in the single unit, and it is a mechanism to judge the pass/fail by the position of the screw of the inspection partner in relation to how far it is screwed.
In addition, there is no classification for machining and inspection.
▽ Reference: TG (tapered screw for pipe gauge )
How to use tapered pipe screw gauge (plug)
| Conventional JIS Standards PT gauge |
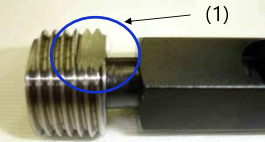 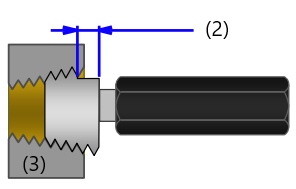 (1) Notch (2) Passing range (3) internal thread PT gauge has one notch Passes if the pipe end is within the notch range of gauge |
| Current JIS Standards RC gauge |
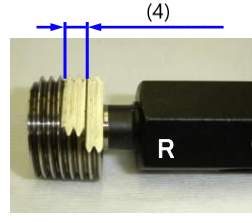 (4) Passing range of R R gauge has two notches |
| Current JIS Standards R gauge |
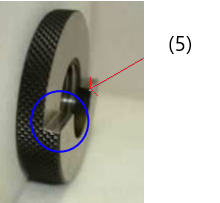 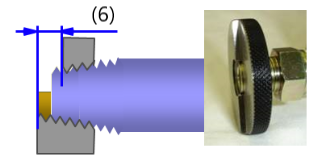 (5) Notch (6) Passing range There is no classification between Rp and Rc gauge ! (Both use R) If the end face of the external thread stops between the notches, it passes. |
Shape of tapered screw gauge (ring) for pipe
* There is a difference in the number of notches in the plug gauge between PT and R, but there is no difference in the number of notches in the ring gauge . There is a difference in the thickness of the gauge . (PT is thicker than R.) )
| Conventional JIS Standards PT gauge |
Current JIS Standards (ISO Standards) R gauge |
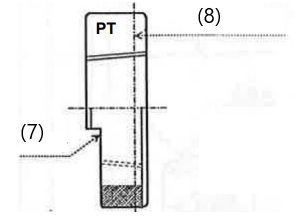 (7) Notch (8) Position of reference diameter |
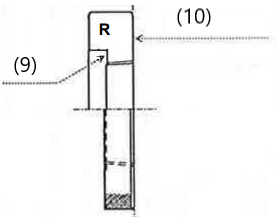 (9) Notch (10) Position of reference diameter |
The tapered screw gauge has no passing or stopping setting, and there is no distinction between machining and inspection! No precision!
(FAQID:237)